
Benefits
Standard maintenance work on gearbox of a wind turbine necessitates the partial disassembly of a large, heavy casting within a small space at top of tower. Carrying the necessary equipment to the top and completing the work requires four technicians to work five 12-14 hour days. Goal of project is to reduce time, reduce cost, and improve safety of workers.
Purpose
Redesign gantry crane system to reduce time, manpower, and cost to complete NGC gearbox maintenance in GE Wind Turbines.
Current Design
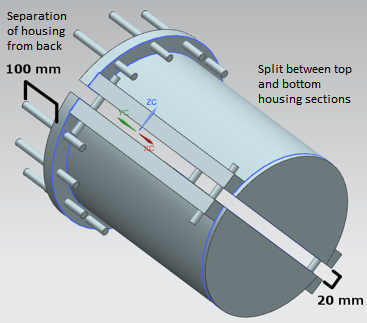
- A NGC gantry crane is used to move the gearbox’s casing (2MN) to access the high speed shaft (HSS) and subsequent rebuild/alignment
- Casing moves 100mm forward and separate top half 20mm up for process
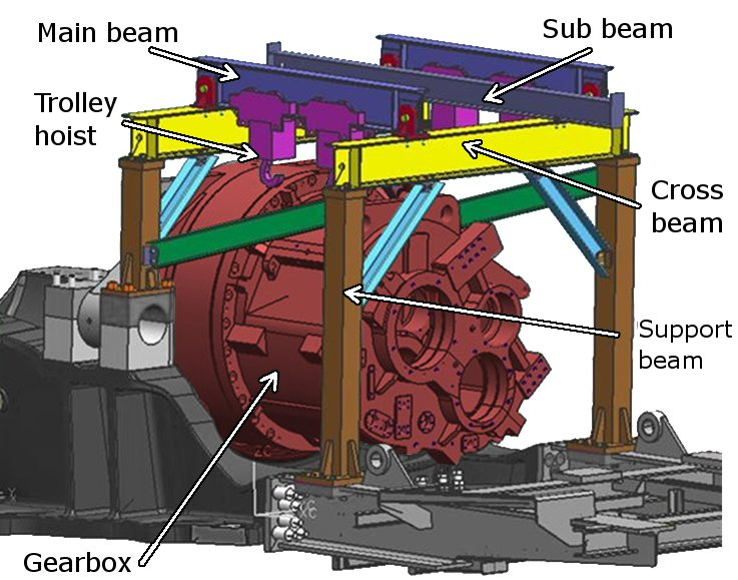
Alternative Approaches
Cable Suspension
- Replace main beams in current gantry crane with cables
- Reduced size and weight of other crane members
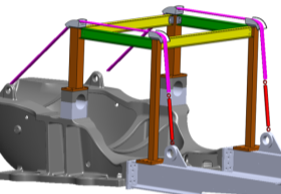
- Pros
- Reduced weight
- Increased maneuverability
- Reduced installation time
- Cons
- Higher occupational risk
- Inspection for cable fatigue
Bolt Supported
- Replace bottom half bolts in casing, function like cantilever beams
- Use 2 heavy duty jib cranes to help support housing
- Slide casing on bolts
- Cons
- Housing binding on bolts
- Realigning housing with gearbox components
Conclusions
- Both designs are feasible, safe, and provide promising solutions
- Bolt supported system offers greatest cost and time savings
- 50% manpower reduction
- 75% equipment cost reduction
People
Casey Hoffman
Aren Paster
Research Area
Manufacturing, Automation, and Control
Project Type
Manufacturing
Funding Agency/Sponsor
General Electric
